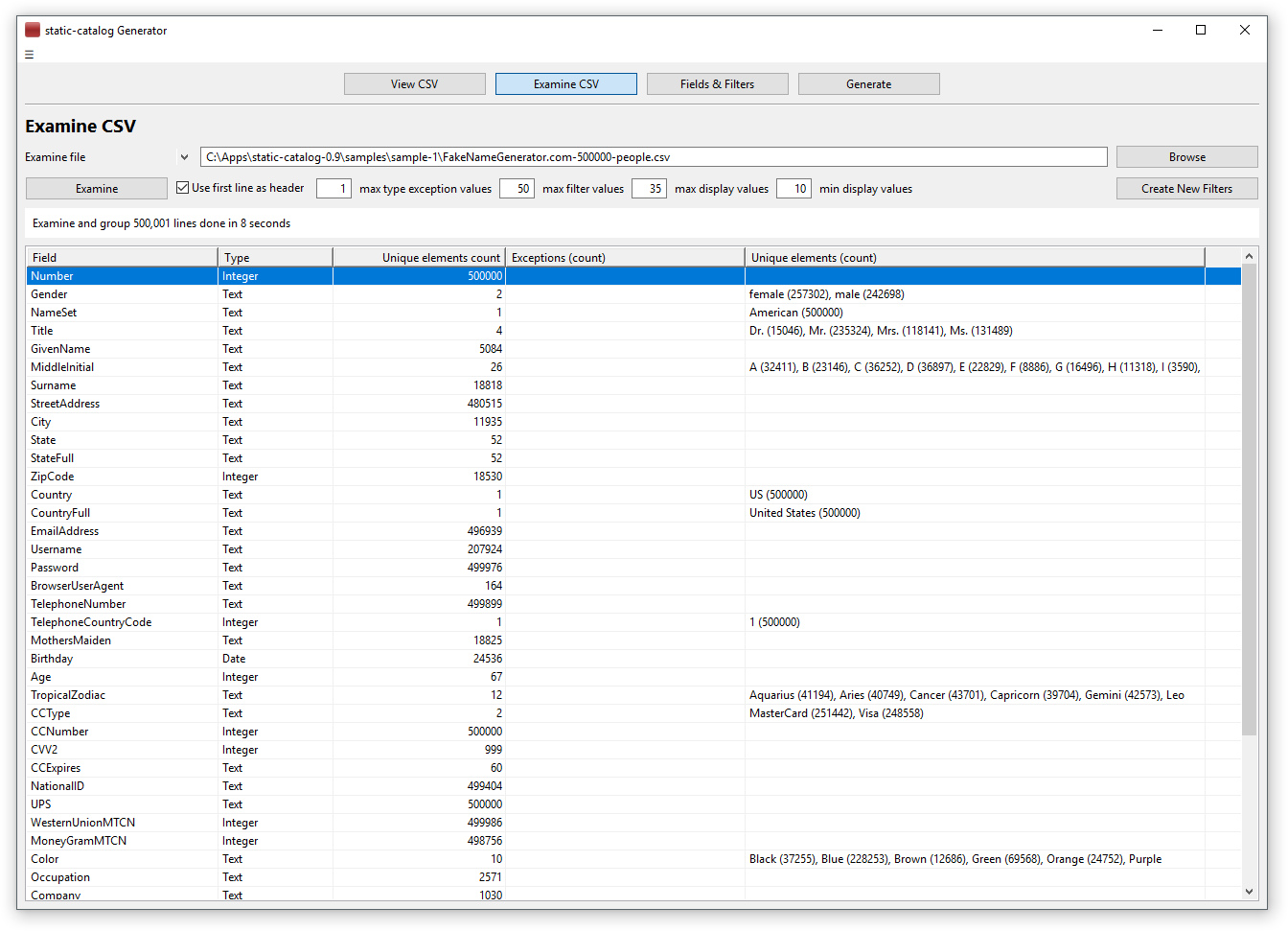
Examine the source CSV data
The source CSV file is made up of columns (fields) of data, each one having a specific data type. In order to find the data types, the file should be loaded in the second tab of the application and examined. Once examined, it will show in the result grid:
- On the first column, the name of each field taken from the first line of the file
- On the second column, the type of the field
The type of the field is found by analyzing the data. However, we can have all the values of a field being the same data type, EXCEPT for a small number of them representing something else. The most frequent example is when the value is empty, it will be treated as an exception of the rest of the data. Another example is the value “NULL” or “N/A” (not available) or “All” or “none”, any of these can be treated as exception if the rest of the data have the same type. So, the first thing to do is set the maximum number of such distinct values that can be found and considered exceptions, by default this number is 1
Considering as “values” all the rest of non-exception values found for a field, the types will be set as follows:
- If all the values can be converted to date, then the field type is “Date”
- If all the values can be converted to double, then the field type is “Real”
- If all the values can be converted to an integer, then the field type is “Integer”
- If the values cannot all be converted to one of the above, the type is “Text”
In order to use a field as a filter, the number of its distinct values must be known, and it is displayed next. For a filter to be used by a user it must have a reduced number of values, usually less than 100 (default 50) because more would be difficult to understand. For the fields with less distinct values than the maximum filter values, the values will be displayed next with the count for each value. First will be displayed the exceptions (if exists – and will always be the first on the filter) and then all the values (double click to see them all)
Here and in the rest of static-catalog unless specifically stated otherwise the values will be sorted by “natural-sort”, this means that numbers will be considered numbers even inside the words (“a2” will be before “a10”)
By changing the number of exceptions and maximum filter values, the file can be examined to see the most appropriate way to have value filters. Where in doubt, go back to the previous tab and see how the file looks like
In order to help the page generation in the next steps, here two global parameters can be set about how many values can be shown to the user, and if there are more values how many values to show until having a “more” button or a similar function. These values can be changed for each field in the next step
Once satisfied with the examination, by pressing “Create New Filters” a fields-filters file will be created and opened in the next tab
The missing piece of static generated sites.
static-catalog.org - 2019